PBS | NOVA Documentary
patents.google.com
WHAT IS CLAIMED IS:
A system for delivering audio content to a user during a dream state, the system comprising: a plurality of electrodes positionable on the head of the user, the electrodes configured to detect electrical signals of the user’s brain or head indicative of the dream state; logic resources operably coupled to the plurality of electrodes, the logic resource configured to analyze the electrical signals to determine when the dream state occurs; an audio storage device operably coupled to the logic resources; the storage device configured to store audio content to be delivered to the user; and an audio output device coupled to at least one of the logic resources or the audio output device, the audio output device configured to output an audio signal to the user containing the audio content.
- The system of claim 1 , further comprising circuitry for processing the electrical signals.
- The system of claim 2, wherein the processing circuitry comprises an amplifier or an operational amplifier.
- The system of claim 2, wherein the processing circuitry comprises a filter, a high pass filter, a low pass filter or a band pass filter.
- The system of claim 2, wherein the processing circuitry comprises an signal converter, an AID converter or a D/A converter.
- The system of claim 1 , where the audio output device comprises an earpiece or headphones.
- The system of claim 1 , where the audio output device comprises an external device.
- The system of claim 7, where the audio output device is wireiessly coupled to at least one of the logic resources or the audio storage device.
- The system of claim 8, where the audio output device is a speaker in a portable electronic device, ceil phone or tablet device.
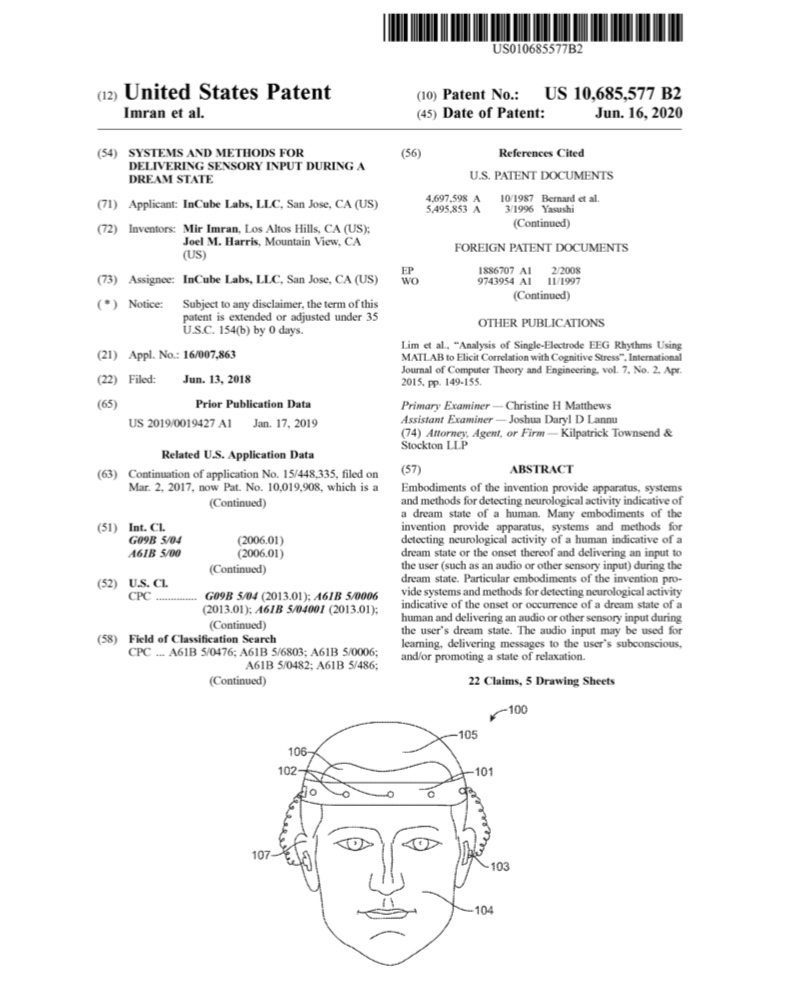
- The system of claim 1 , wherein the plurality of electrodes are disposed on a flexible material which bends and fixes with movement of the user’s head to maintain electrical contact of the electrodes with the user’s skin during movement of the user’s head.
- The system of claim 1 , further comprising a headband device configured to be worn on the user’s head, the electrodes disposed on the headband.
- The system of claim 1 1 , wherein the headband is configured to bend and flex with movement of the user’s head to maintain electrical contact of the electrodes with the user’s skin during movement of the user’s head.
- The system of claim 1 1 , wherein the plurality of electrodes are disposed on an interior surface of the headband.
- The system of claim 1 1 , wherein at least one of the logical resources, audio storage device and audio output device are attached to the headband.
- The system of claim 1 1 , wherein the audio output device is integral to the headband.
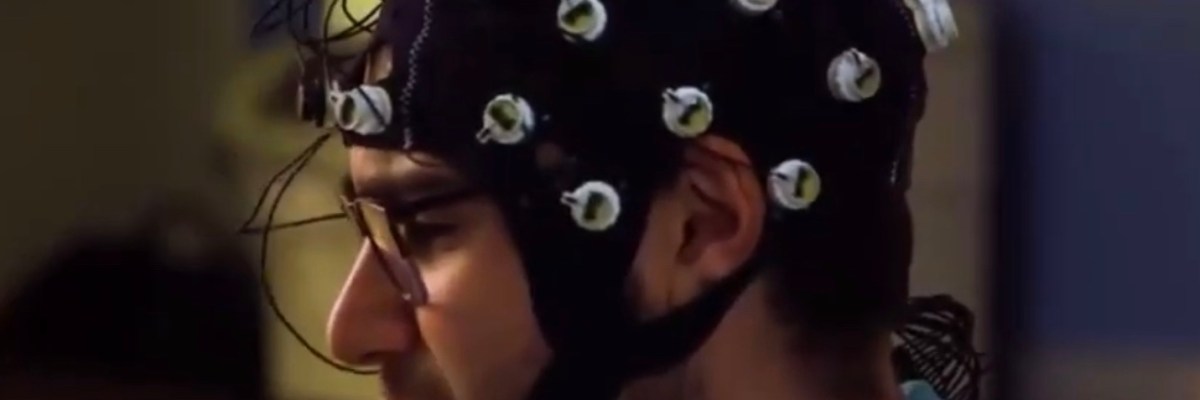
- The system of claim 1 , wherein at least a portion of the plurality of electrodes are configured to detect saccadic eye movement of the user indicative of a dream state.
- The system of claim 16, wherein the plurality of electrodes includes a first portion configured to detect saccadic eye movement of the user indicative of a dream state and a second portion configured to detect electrical activity of the user’s brain indicative of the dream state.
- A system for delivering audio content to a user during a dream state, the system comprising: a plurality of sensors positional on the skin of the user, the sensors configured to detect a condition of the users skin indicative of the dream state; logic resources operably coupled to the plurality of sensors, the logic resource configured to analyze inputs from the sensors to determine when the dream state occurs; an audio storage device operably coupled to the logic resources; the storage device configured to store audio content to be delivered to the user, and an audio output device coupled to at least one of the logic resources or the audio output device, the audio output device configured to output an audio signal to the user containing the audio content.
- The system of claim 18, wherein the sensors are temperature sensors configured to detect a temperature of the users skin.
- The system of claim 18, wherein the sensors are impedance sensors configured to detect an impedance of the users skin.
- The system of claim 8, wherein the sensors positioned on the head of the user.
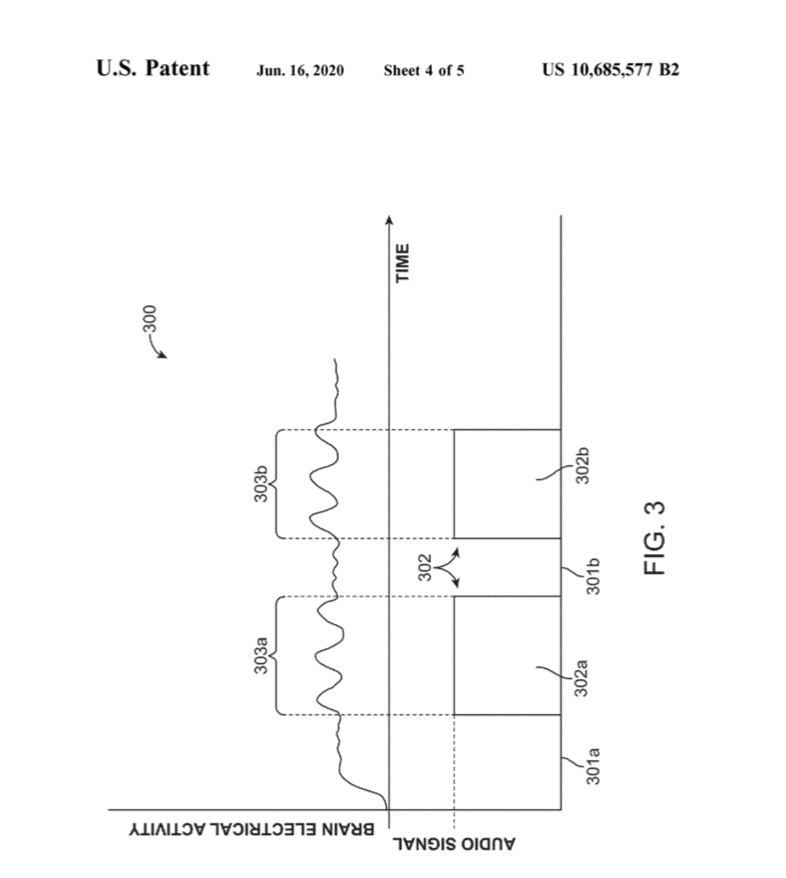
- A method for delivering to an audio input to a user during a dream state, the method comprising: detecting electrical activity of a user’s brain or head indicative of a dream state or the onset of a dream state; and delivering audio input to the user in response to the detection of the electrical activity indicative of the dream state.
- The method of claim 22, wherein the audio input comprises spoken words.
- The method of claim 23, wherein the spoken words contain content used for learning by the user.
- The method of claim 24, wherein the spoken words comprise a lecture on a subject to be learned by the user.
- The method of claim 22, wherein the dream state corresponds to a REM sleep state.
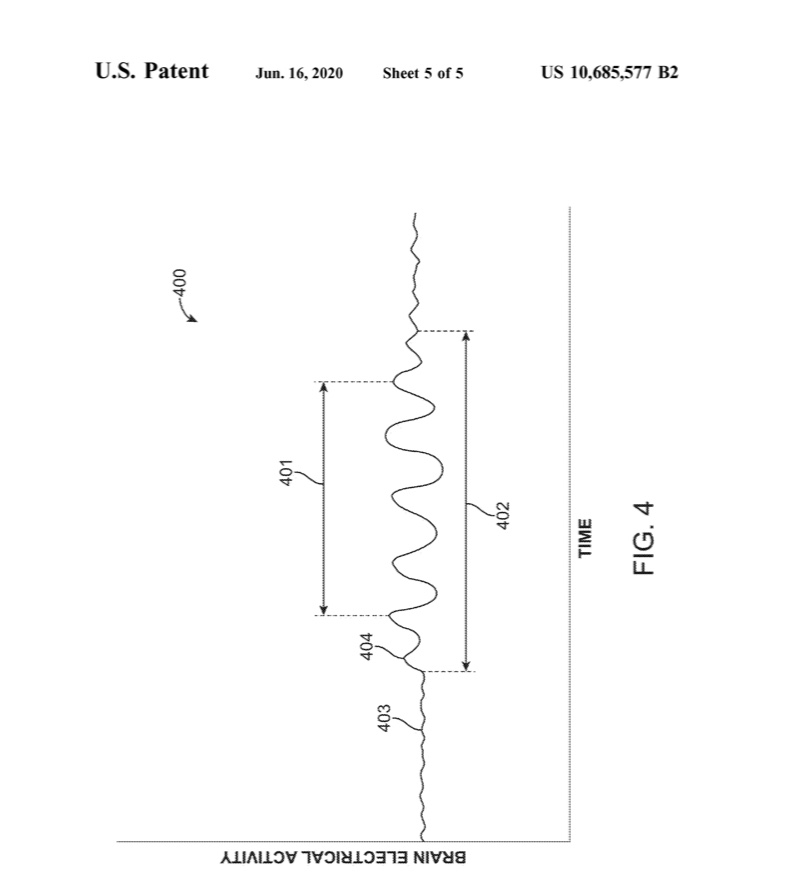
- The method of claim 22, wherein the electrical activity indicative of the dream state comprises alpha brain waves.
- The method of claim 22, wherein the electrical activity of the user’s brain is detected using electrodes positioned on the user’s head.
- The method of claim 28, wherein the electrodes are placed In a pattern on the users head to facilitate detection of electrical activity indicative of the dream state.
- The method of claim 28, wherein the electrodes are positioned on the user’s forehead or face.
- The method of claim 28, wherein the electrodes are positioned on headband device worn by the user.
- The method of claim 22, further comprising: detecting electrical activity of the user’s brain indicative of a period of optimal receptivity by the user to content contained in the audio input; and wherein the audio input is delivered during the period of optimal receptivity.
- The method of claim 32, wherein the electrical activity of the user‘s brain indicative of the period of optimal receptivity comprises brain waves or alpha brain waves.
- The method of claim 33, wherein the brain waves maintain a frequency between about 7.0 to 12 Hz.
- The method of claim 33, wherein the brain waves maintain a frequency between about 7.5 to 1 .5 Hz.
- The method of claim 33, wherein the brain waves maintain a frequency between about 7.0 to 8.0 Hz.
- The method of claim 32, wherein the period of optimal receptivity comprises a portion of a period of a REM sleep state.
- The method of claim 37, wherein the portion of the period of the REM sleep state comprises the beginning, middle or end of the period.
- The method of claim 22, wherein the dream state is detected by detecting a period of decreased motor activity of the user.
- The method of claim 22, wherein the dream state is detected by detecting a period of increased motor activity followed by a period of decreased motor activity.
- The method of claim 22, wherein the electrical activity detected is associated with movement of the user’s eyes.
- The method of claim 41 , wherein the electrical activity detected is used to detect saccadic eye movement of the user associated with a dream state.
- The method of claim 41 , wherein the electrical activity detected also comprises neurological activity of the user’s brain and wherein the dream state is detected based on analysis of the neurological activity of the user‘s brain and movement of the user’s eyes.
- The method of claim 43, wherein the movement of the detected movement of the user’s eyes is saccadic eye movement associated with a dream state.
- A method for delivering to an audio input to a user during a dream state, the method comprising: sensing electrical activity of the user’s brain; determining if the user is in a dream state or onset of a dream state based on analysis of the sensed electrical activity of the user’s brain, and delivering audio input to the user in response to the determination of the dream state or dream state onset.
- The method of claim 45, wherein the user being in the dream state or dream state onset is determined by detecting a period of decreased motor activity of the user.
- The method of claim 45, wherein the period of decreased motor activity is detected using an accelerometer positioned on the user.
- The method of claim 45, wherein the determination of the user being in dream state or dream state onset is performed using logic resources.
- The method of claim 45, wherein the logic resources are wirelessly coupled to at least one of a device for sensing electrical activity of the users brain or a device for delivering the audio input.
- The method of claim 45, wherein the determination of the user being in dream state or dream state onset is performed remotely to the user.
- The method of claim 45, wherein the determination of the user being in a dream state or dream state onset is made by comparing a pattern or waveform of the electrical activity of the users brain to a stored pattern or waveform.
- The method of claim 45, further comprising: determining a period of optimal receptivity by the user to content contained in audio input; and wherein the audio input is delivered during the period of optimal receptivity.
- The method of claim 52, wherein the determination of the period of optimal receptivity is made based on analysis of sensed electrical activity of the user’s brain when a test acoustic output signal is delivered to the user’s ears.
- A method for delivering to an audio input to a user during a dream state, the method comprising: sensing electrical activity associated with movement of the users eyes; determining if the user is in a dream state or onset of a dream state based on analysis of the sensed electrical activity, and delivering audio input to the user in response to the determination of the dream state or dream state onset.
- The method of claim 54, wherein the sensed electrical activity is used to detect saccadic eye movement of the user associated with a dream state.
Categories: Lifestyle























1 reply »